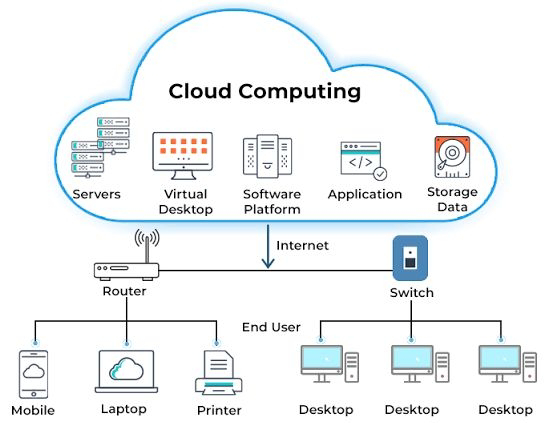
Cloud Computing Paradigm
- From one computer, we have learnt how to use multiple computers to solve large scale problems using the Internet as our communicating medium.
- Our applications have become more data-intensive and network-centric. All these have helped to solve larger computational problems that have become the need of the day
- The ability to grow and shrink if required, is known as scalability. With the advent of computing technology, we need to have scalability that will accommodate the changes.
- Web hosting is the mechanism of providing space in the World Wide Web (WWW) to host one's web resources. However, such service offerings suffered from the problem of scalability, which was mitigated by the user of virtualization.
Here is a Presentation on Cloud Computing.
Scenario Prior to Cloud Computing:
- Prior to cloud computing, users of computing devices are supposed to invest money on computing resources such as hardware, software, networking, and storage.
- The investment on IT resources requires a lot of money for its users as they have to buy these computing resources, keep them in their premises, and maintaining them to make them operational.
- The upfront cost will become a huge expenditure to an organisation that requires enormous computing and storage resources.
- In traditional on-premise model, the consumer is responsible for purchasing and maintaining all of the IT infrastructure. This can be a significant upfront cost, but it can also give the consumer more control over their IT environment. There are also ongoing costs associated with staffing, hardware and software maintenance, and facilities maintenance.
- In cloud computing model, the provider manages most of the IT infrastructure. This includes purchasing and maintaining hardware, software, data centre space, power, cooling, and IT staff. Cloud users typically pay a monthly fee for the resources they use.
Motivation for Cloud Computing:
- In cloud computing, users of computing devices (storage and CPU) can avail them from a service provider called Cloud Service Provider (CSP) as and when needed and pay only for the duration of their usage.
- This would cost only a reasonable investment or spending, compared to the huge investment required for buying the entire computing infrastructure.
- The cloud represents Internet-based computing resources which are made available to the general public or an individual through some secured network connectivity.
Usage of Cloud Computing in an Enterprise
- In this model of computing, an organisation's core computing power resides offsite and is essentially subscribed to rather than owned.
- Cloud computing has the power to bring the computing resources (CPU, storage etc.) to an organisation or an individual without the need for capital investment, instead just by hiring them online from a service provider and paying only for the consumed services.
Need for Cloud Computing:
- In an organisation, cloud computing is needed in getting the services of computing resources at the user level at an operational cost. This results in saving a lot of money by eliminating the upfront cost - cost involved in setting up and running IT resources on the premise.
- Cloud computing encompasses the subscription based or pay-as-you-go service model for offering computing to end users or customers over the Internet and thereby extending the IT's existing capabilities.
- Cloud computing makes our life easy in the field of computing by providing resources available on the computer over the Internet . As end users, we need to know how to tap into the resources available on the cloud through a system which is connected to Internet.
- Reliability is another major benefit of using cloud computing in our day to day lives. On the cloud, losing our data/file is much less likely. However, just like anything online, there is always a risk that someone may try to gain access to our personal data.
- Now-a-days, cloud computing is growing in popularity, especially among individuals, and Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs).
Definition of Cloud Computing:
- In the simplest terms, cloud computing is a kind of distributed computing in which storage and processing of data or application take place over the Internet on a remote machine instead of doing them on the local machine. The term cloud is just a metaphor for the Internet in this definition.
- When we store and run a program from the local computer's hard drive, that scenario is called on premise storage and computation. That means, we have our own resources such as CPU and storage device for performing computation and storage on premise.
- Whereas, in cloud computing users are allowed to store and process data or programs on a computer running remotely (on the cloud) over the Internet. With an online connection, cloud resources such as computing power (CPU), storage capacity (hard disk), networking features and application software such as ERP can be availed from anywhere, anytime and at any device.
- Here is a simple definition of Cloud Computing: "Cloud Computing is a type of Computing System In which High Performance Computing resources (such as servers, application and networking) are available to its users over the Internet."
NIST Definition of Cloud Computing:
- The formal definition of cloud computing comes from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) as follows:
"Cloud computing is a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. "
- It means that the computing resource or infrastructure - be it server hardware, storage, network, or application software - all available from the cloud vendor or provider's site/premises, can be accessible over the Internet from any remote location and by any local computing device.
- In addition, the usage or accessibility is to cost only to the level of usage to the customers based on their needs and demands, also known as the pay-as-you-go or pay-as-per-use model.
- Minimal management effort implies that at the customer's side, the maintenance of computing systems is very minimal as they will have to look at these tasks only for their local computing devices used for accessing cloud-based resources, not for those computing resources managed at the provider's side.